What is construction & demolition waste?
Common industrial waste (CIW) or post-consumer waste (PCW) is all of the waste generated by companies, manufacturers, retailers, craftspeople and service providers. Industrial waste is primarily the product of administrative and office activities (equipment, furniture, consumables, packaging), general building and green space maintenance, waste produced by worksites and by production and maintenance operations.
Industrial waste consists essentially of metals, paper and cardboard, glass, textiles, wood, plastics, etc., and it is highly recoverable. Lastly, part of the post-consumer waste that is rejected as industrial waste can be turned into SRF. In other words, it can used as the basic ingredient for producing solid recovered fuel (SRF).
The bulk of construction waste consists of inert waste ; the remainder can be treated as industrial waste. Inert waste is made up of stones, earth and excavated material, concrete, bricks, roof tiles, wall and floor tiles, paving, plaster, etc.
This inert waste, once cleaned, can be used as quarry filling. The other recoverable materials are generally sent to the appropriate treatment channels.
What is construction waste?

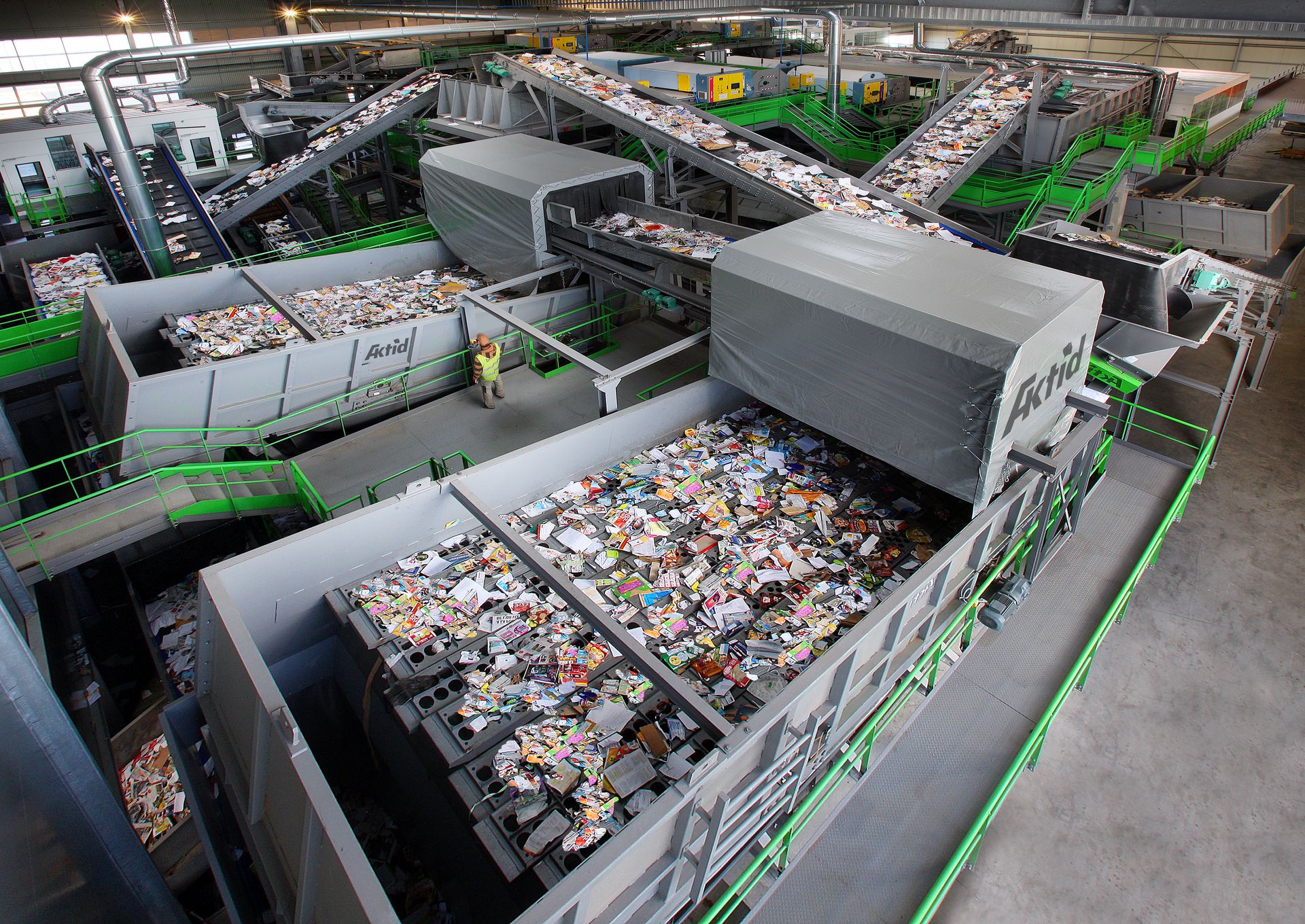
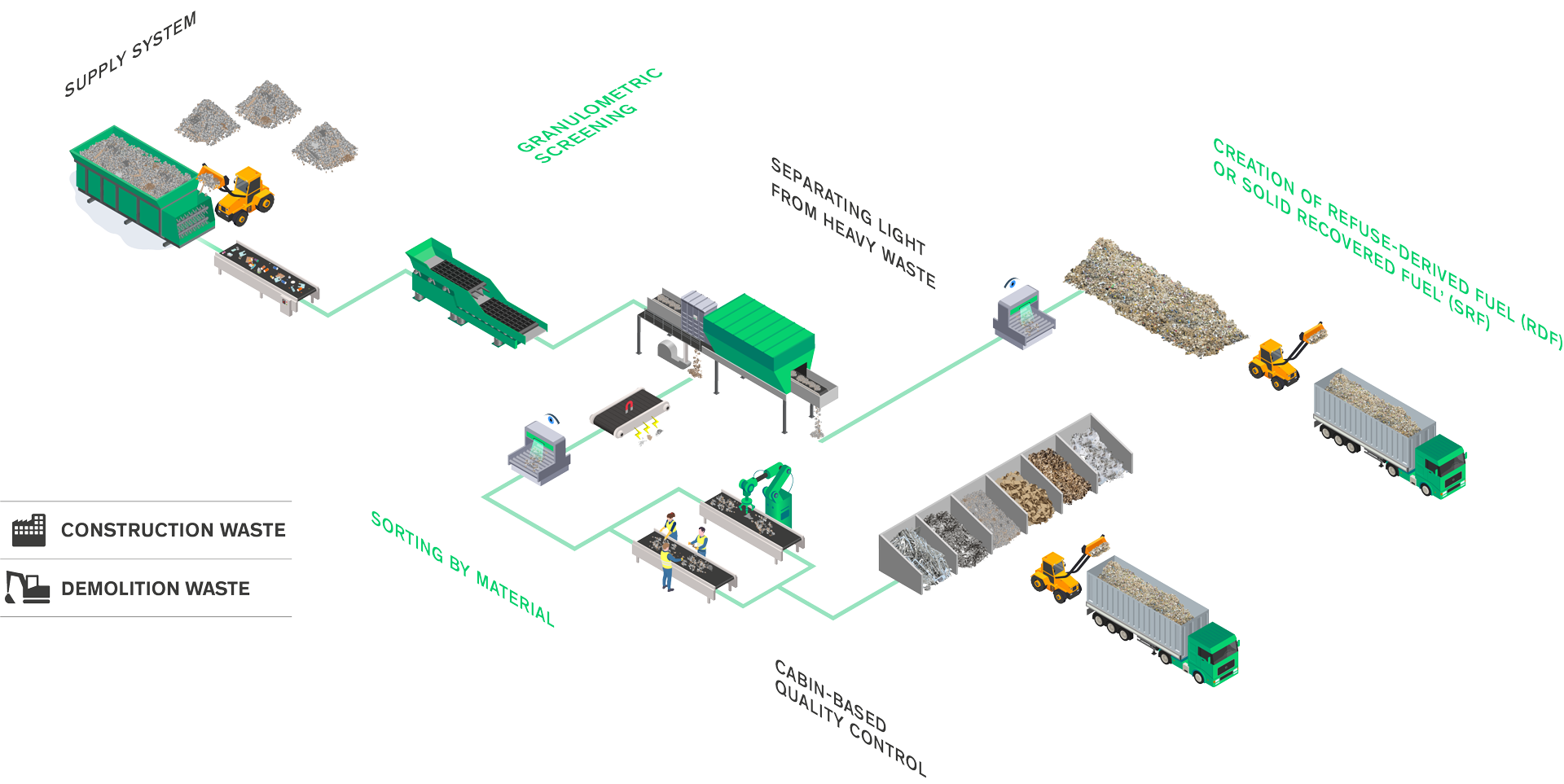
The main stages in sorting industrial waste
and construction & demolition waste (C&D)
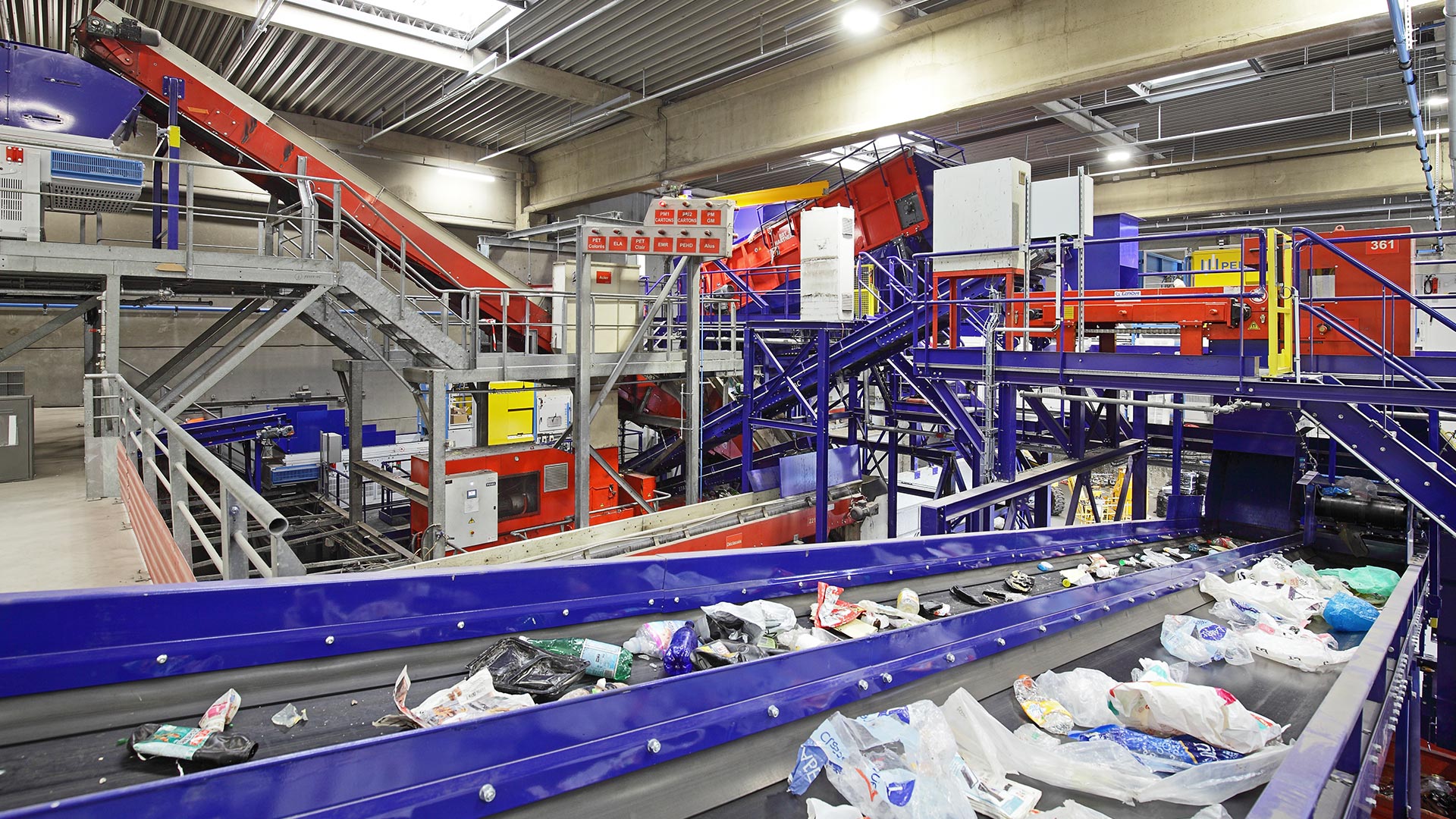
Next, the flow is “cleaned” by an aeraulic separator that sucks up the light items of waste. The heavy items move on to step 4 (sorting by material), while the light waste can be sent for processing into solid refuse-derived fuel (RDF).
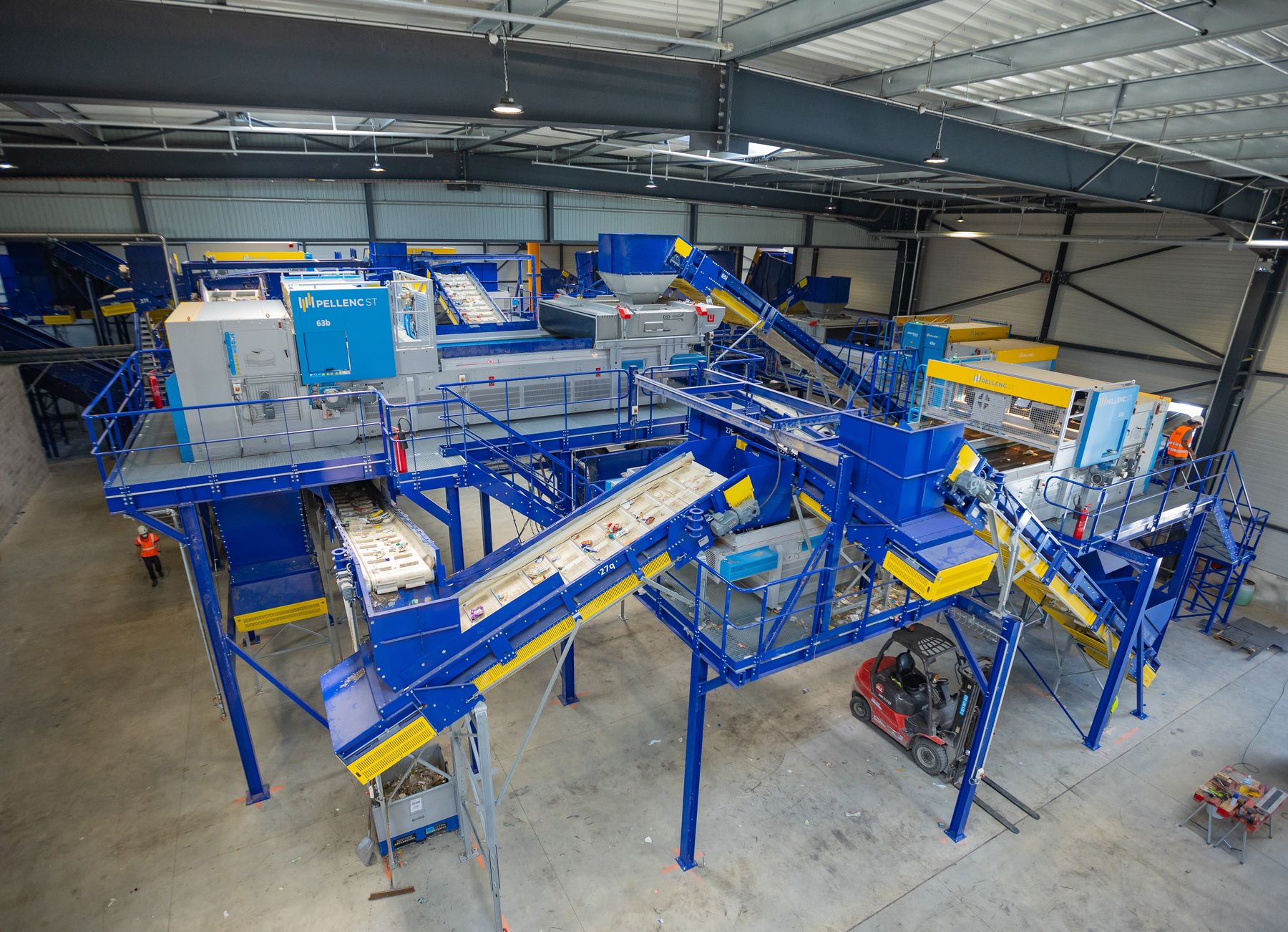
A combination of optical sorting machines makes it possible to recycle or reuse the different materials (wood and plastic in the case of industrial waste, for example; bricks and plaster in the case of C&D waste, etc.). Overbands and eddy current separators make it possible to recycle the various metals.
We often recommend a cabin-based quality control to optimise the recovery rate. It can be carried out manually or in combination with robots developed specifically for sorting bulky and heavy wastes.
For some types of waste, and in particular industrial waste, it can be viable to work on the flow of light waste items with a view to processing them into refuse-derived fuel or solid recovered fuel. If so, an optical sorting machine and a metal detector are necessary to extract PVC and residual metals from the waste flow.
Sorting facilities in a variety of formats
Depending on the type of incoming waste, the type of outlets considered and the investment capacities, the facilities for sorting post-consumer waste or construction waste may display more or less complex variations, comprising all or only some of the steps presented above. The AKTID team will present the various possible options to you and provide the guidance you need to define the solution best suited to your project.
An AKTID sorting facility for post-consumer or construction waste brings you :
AKTID facilities
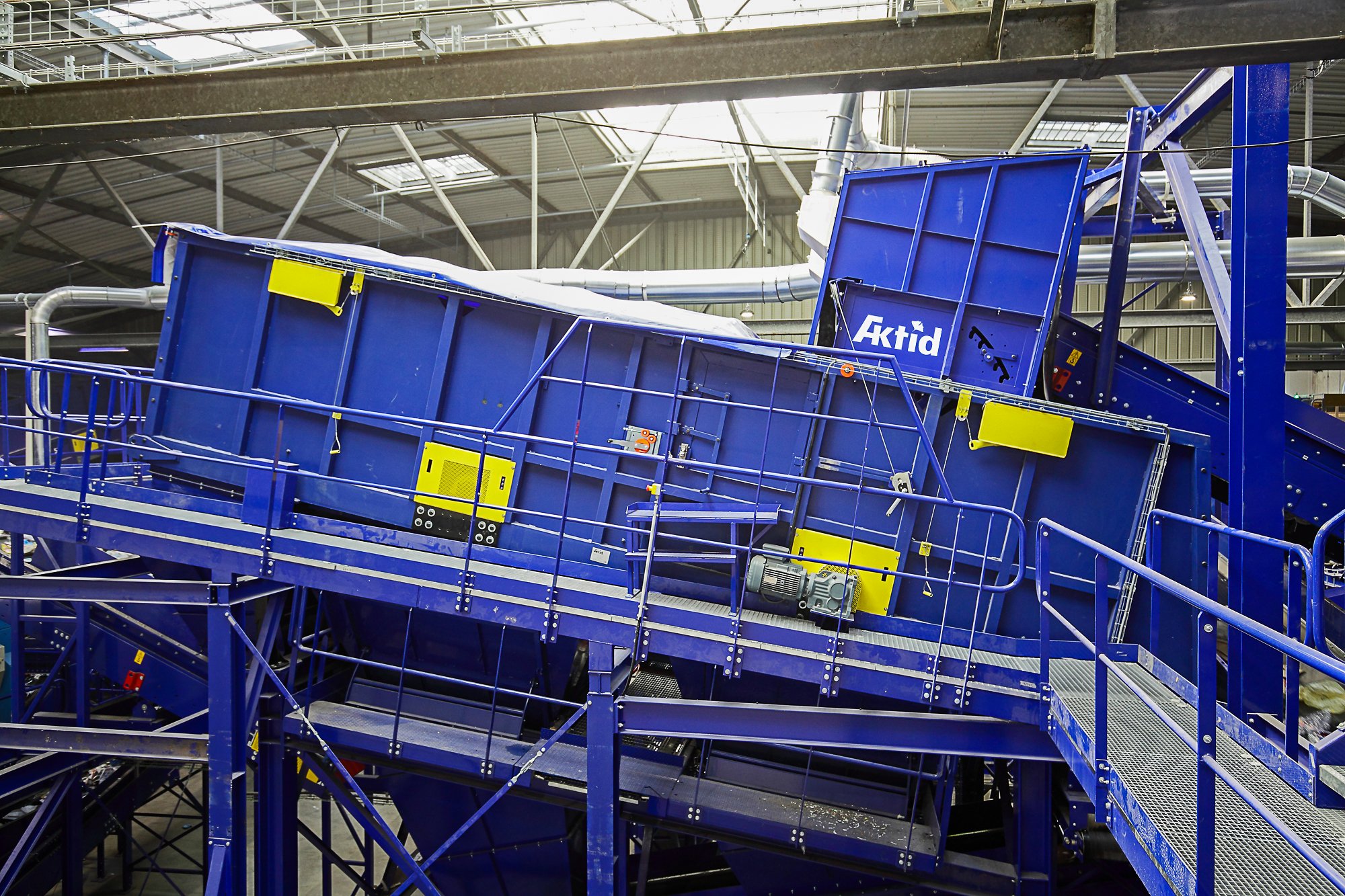
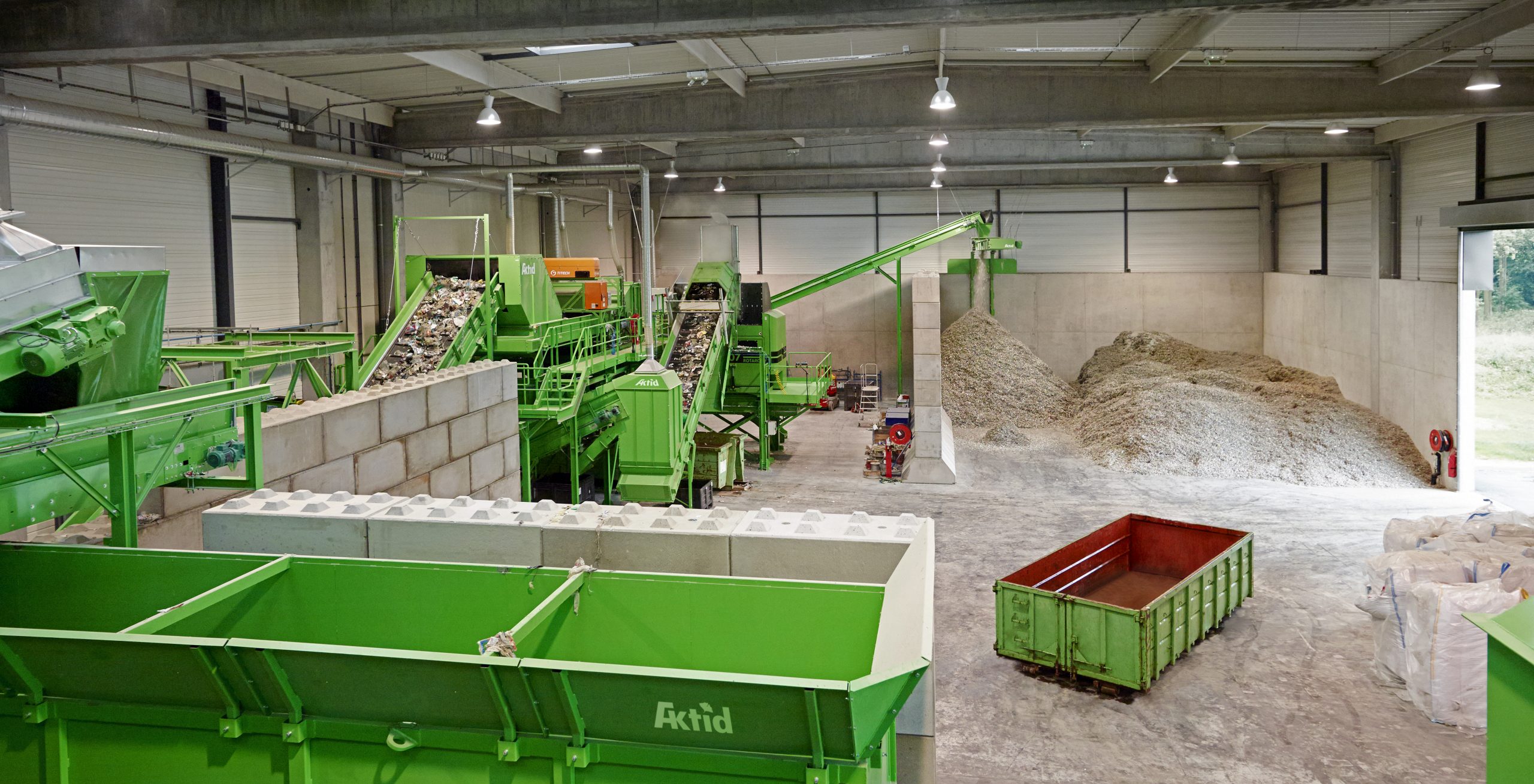
Close-up on : Vibratory screens for heavy waste
ACTION EQUIPMENT, a US-based manufacturer of vibratory machines for over 40 years, has for many years been AKTID’s exclusive partner for the European market.
Its TAPER-SLOT® vibratory screen delivers outstanding robustness and efficiency.
AKTID incorporates it into all of its sorting facilities for heavy or complex waste, such as industrial, bulky or combustible waste, construction waste, wood, tyres or metals, etc.
The screen meshes’ patented design, combined with the unparalleled vibration amplitude, make it possible to position this machine with a slight tilt.
As a result, the materials spend much longer in the machine, they are separated out as efficiently as possible and there is very little snagging or congestion.
Close-up on : Flip-flow vibratory screens for fine and damp materials







Stay In Touch